

- Search nucleotide sequence on clc main workbench plus#
- Search nucleotide sequence on clc main workbench download#
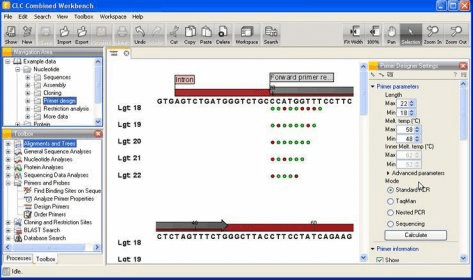
Toolbox | Sequencing Data Analysis | Assemble sequences De novo assembly: common in the cases that you do not have a reference sequence to the sequenced data.Comparison with a similar sequence obtained from a sequence database Or Assembly can be done to a reference sequence.Assembling the two sequences aligns the sequences where they overlap to get a contiguous sequence called a contig. Assemble sequences: In most cases forward and reverse primers are used, hence on sequencing you end up with a forward and reverse sequence.These annotated sections are ignored in further analysis. When the trimming is done the parts of the sequences that are trimmed are not actually removed but trim annotations are saved to the sequences. Click next and choose to save the results.If the sequences were cloned products select the vector trimming options.Specify the trimming parameters the limit on trim quality scores can be increased or reduced to make trimming more or less stringent respectively.Select all the sequences to be trimmed on the left panel and use the arrow to move them to the right panel, click next.This gives the trim sequences dialogue box.
Sequencing Data Analysis | Trim Sequences Trimming eliminates reads of poor quality (and in the case of cloned inserts removal of vector contamination).
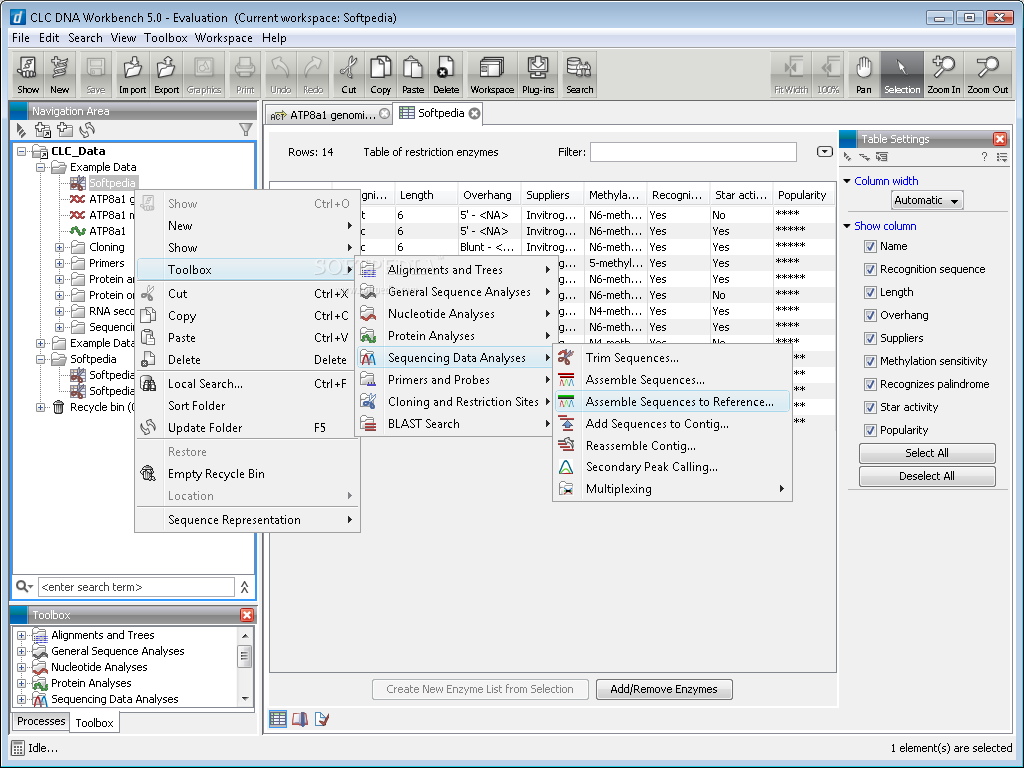

The user interface of CLC is as below: there is Navigation area and a View area.
Search nucleotide sequence on clc main workbench download#
Download the workbench from the link provided above.
Search nucleotide sequence on clc main workbench plus#
It consists of a multiple sequence alignment of sequence reads plus a consensus sequence.Ĭonsensus sequence: A sequence of nucleotides in common between regions of homology in related DNA sequences. This can be more difficult if the region of overlap is very small.Ĭonflict: a nucleotide position in the assembled sequence overlap which has different bases, or where there is a gap on one sequence and a base at the corresponding position on the other sequence.ĭNA Contig: Contiguous sequence of DNA created by assembling overlapping DNA sequence reads. Sequence assembly: aligning and merging fragments of a much longer DNA sequence in order to reconstruct the original sequence.Īssembly to a reference sequence: assembly of the sequenced fragments using a similar sequence (a reference sequence) as a guide.ĭe novo assembly: assembly using only your sequenced fragments.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
